The Fmri Technique Makes Use of Activity-dependent Changes in:
- Momentary decrease in blood oxygenation immediately after neural activity increases known as the initial dip in the haemodynamic response function HRF. These measures have a uniformly high spatial resolution of millimetres or less but poor temporal resolution about 1s at best.
Not fMRI or position spec.
. Hyder and Rothman 2012. Metabolic activity Oxygen exchange OD. Functional magnetic resonance imaging measures activity-dependent changes in blood oxygenation.
Functional magnetic resonance imaging fMRI is a neuroimaging technique gaining greater momentum and use by professionals since its invention in 1990. The fMRI technique makes use of activity dependent changes in. The Limitations and Reliability of fMRI.
Single-cell recordings primarily measure the brains A. FMRI doesnt make use of any invasive techniques such as injecting radiolabelled material. FMRI stands for functional magnetic resonance imaging and is a technique used by scientists and medical professionals to map activity in the brain.
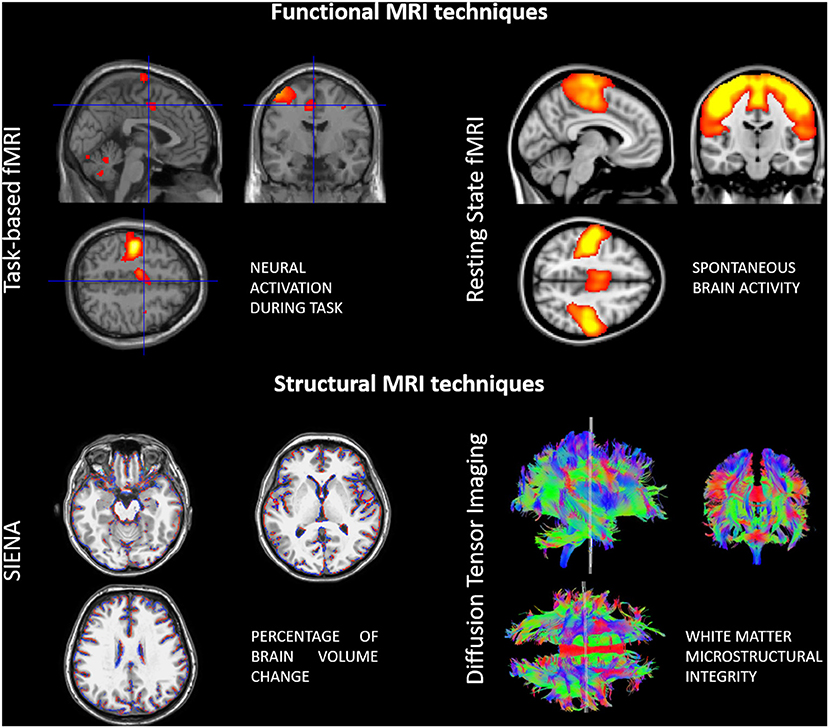
The related techniques of event-related task-based fMRI resting-state fMRI rs-fMRI and real-time fMRI rt-fMRI are widely used in research. A In the control state the arterial supply is. - Relative levels of deoxyhaemoglobin change from regional cortical activity.
Functional MRI has grown from the conjunction of two phenomena. When our brains are active such as when we talk or complete a math problem the parts of the brain that are being used require more energy in the form of glucose. Ultimately because feasible fMRI techniques all depend on the neurovascular response still deeper understanding will be needed of the geometry of the cortical and subcortical microvasculature the molecular signals relating neural electrical activity to vasodilation and vasoconstriction the spatial distribution of pericytes the details of oxygen extraction and the.
Blood flowing through the brain carries oxygen on molecules called hemoglobin. At present fMRI is the most widely used neuroimaging method due to the availability of MRI scanners and a relatively cheap rate per scan. Allows the production of a structural map of the brain without opening the.
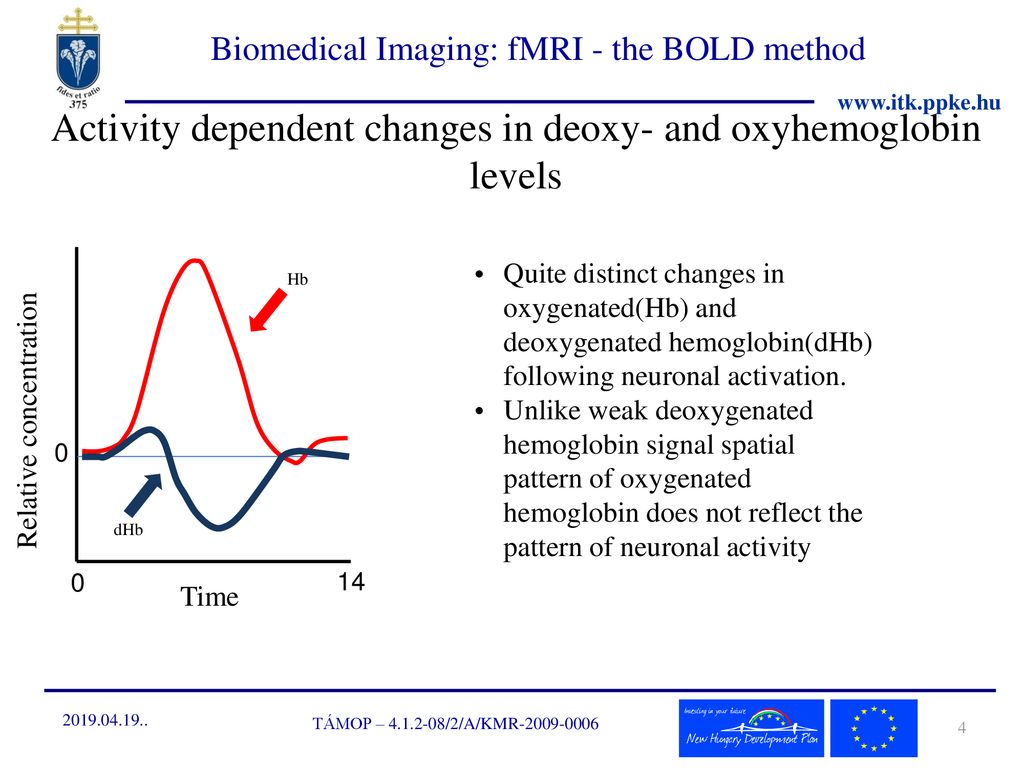
When an area of the brain is in use blood flow to that region also increases. This somewhat paradoxical blood oxygenation level dependent BOLD effect is the basis for fMRI. In addition to the above a few radical fMRI approaches have tried to resolve endogenous activity-dependent brain signals arising from non-hemodynamic sources such as diffusion changes Le Bihan 2007 neuronal magnetic fields Bandettini et al 2005 and metabolite-dependent spectroscopic signals Mangia et al 2009.
Functional magnetic resonance imaging fMRI is an MRI procedure that measures brain activity by detecting associated changes in blood flow. Question 5 2 2 pts The fMRI technique makes use of activity-dependent changes in. FMRI can measure rapid changes in neural activity Blache Maloney 2017.
It has been known for more than 100 years that neural activity causes changes in blood flow and. Functional MRI uses the physical phenomenon of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance NMR and the associated technology of Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI to detect spatially localized changes in hemodynamics that have been triggered by local neural activity. Blood-oxygen-level dependent BOLD is the MRI contrast of blood deoxyhaemoglobin first discovered in 1990 by Dr.
A new technique called molecular fMRI has the potential to help bridge this divide. Seiji Ogawa who also recognized the potential importance of BOLD for functional brain imaging with MRI. The fMRI technique makes use of activity-dependent changes in.
Measures brain activity detecting changes due to blood flow. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging fMRI is a class of imaging methods developed in order to demonstrate regional time-varying changes in brain metabolism 3 37 49. These metabolic changes can be consequent to task-induced cognitive state changes or the result of unregulated processes in the resting brain.
Functional MRI makes use of a special signal called blood oxygen level-dependent BOLD contrast. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. The fMRI technique makes use of activity-dependent changes in.
Functional magnetic resonance imaging fMRI is a powerful non-invasive tool that visualizes brain activity. Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI fMRI measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. Single-cell recordings primarily measure the brains A.
Imaging procedure in which a computer draws a map from the measured changes in the magnetic resonance of atoms in the brain. Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI fMRI is an MRI procedure that measures brain activity by detecting associated changes in blood flow. FMRI and previously H215 O-PET measures local changes in brain haemodynamics induced by cognitive or perceptual tasks.
When an area of the brain is in use blood flow to that region also increases. The biophysical effect that deoxyhemoglobin has magnetic properties that affect the MR signal and the physiological effect that CBF increases much more than oxygen metabolism as neural activity changes so that the deoxyhemoglobin level changes as neural activity changes. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled.
Conversely EEG and MEG measure instantaneously the current flows induced by synaptic activity. Molecular fMRI is an alternative form of fMRI that monitors brain activity through the use of chemical or genetically-encoded probes designed to sense specific molecular and cellular targets in the brain. - Followed by a period where the blood flow.
Hemoglobin molecules also carry iron and therefore have a magnetic signal. For reasons that we still do not fully understand neural activity triggers a much larger change in blood flow than in oxygen metabolism and this leads to the blood being more oxygenated when neural activity increases. The Blood Oxygen Level Dependent BOLD Response - the basis of fMRI.
Biomedical Imaging Magnetic Resonance Imaging Basics Ppt Download
Frontiers Neuroplasticity And Motor Rehabilitation In Multiple Sclerosis A Systematic Review On Mri Markers Of Functional And Structural Changes Neuroscience
No comments for "The Fmri Technique Makes Use of Activity-dependent Changes in:"
Post a Comment